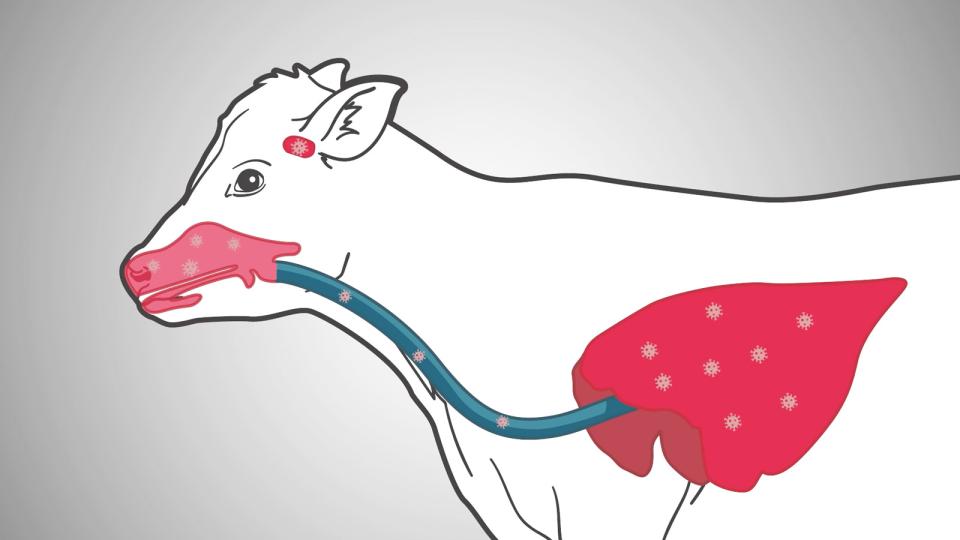
La IBR sigue siendo un contribuyente significativo al complejo de enfermedades respiratorias bovinas y tiene efectos significativos sobre la producción y la fertilidad en los rebaños de ganado. Su síndrome respiratorio clásico con afectación de la conjuntiva y las vías respiratorias superiores sigue siendo reconocible al instante y la naturaleza altamente infecciosa del virus hace que el control frente a un brote sea un desafío. El aspecto típico de latencia del herpesvirus ha hecho que su erradicación sea extremadamente difícil en la mayoría de los países, con solo un puñado de naciones europeas avanzando en los programas de erradicación; sin embargo, el control es posible con protocolos de vacunación semestrales sólidos y vigilancia.
Oliver Maxwell BVSc BSc(Hons) MVM DipECBHM. Especialista en Salud y Producción Bovina por el Real Colegio de Cirujanos Veterinarios. Especialista Europeo en Gestión de Salud Bovina
References:
Ampe B., Duchateau L., Speybroeck N., Berkvens D., Dupont A., Kerkhofs P., Thiry E., Dispas M., 2012.Assessment of the long-term effect of vaccination on transmission of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus in cattle herds hyperimmunized with glycoprotein E–deleted marker vaccine American journal of veterinary research, 73(11), pp.1787-1793.
Brar, J.S., Johnson, D.W., Muscoplat, C.C., Shope Jr, R.E. and Meiske, J.C., 1978. Maternal immunity to infectious bovine rhinotracheitis and bovine viral diarrhea viruses: duration and effect on vaccination in young calves. American journal of veterinary research, 39(2), pp.241-244.
Bosch J.C., De Jong M.C.M., Franken P., Frankenas K., Hage J.J., Kaashoek M.J., Maris-Veldhuis M.A., Noordhuizen J.P.T.M., Van der PoeI W.H.M., Verhoeff J., Weerdmeester K., Zimmer G.M., Van Oirschot J.T., 1998 An inactivated gE negative marker vaccine and an experimental gD-subun:it vaccine reduce the incidence of bovine herpesvirus 1infections in the field. Vaccine, 16, pp.265-271.
Carter, J.J., Weinberg, A.D., Pollard, A., Reeves, R., Magnuson, J.A. and Magnuson, N.S., 1989. Inhibition of T-lymphocyte mitogenic responses and effects on cell functions by bovine herpesvirus 1. Journal of Virology, 63(4), pp.1525-1530.
D’arce, R.C.F., Almeida, R.S., Silva, T.C., Franco, A.C., Spilki, F., Roehe, P.M. and Arns, C.W., 2002. Restriction endonuclease and monoclonal antibody analysis of Brazilian isolates of bovine herpesviruses types 1 and 5. Veterinary microbiology, 88(4), pp.315-324.
Davies, D.H. and Carmichael, L.E., 1973. Role of cell-mediated immunity in the recovery of cattle from primary and recurrent infections with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Infection and Immunity, 8(4), pp.510-518.
Griebel, P.J., Ohmann, H.B., Lawman, M.J.P. and Babiuk, L.A., 1990. The interaction between bovine herpesvirus type 1 and activated bovine T lymphocytes. Journal of General Virology, 71(2), pp.369-377.
Griebel, P.J., Qualtiere, L., Davis, W.C., Lawman, M.J. and Babiul, L.A., 1987. Bovine peripheral blood leukocyte subpopulation dynamics following a primary bovine herpesvirus-1 infection. Viral immunology, 1(4), pp.267-286.
Jones, C., 2003. Herpes simplex virus type 1 and bovine herpesvirus 1 latency. Clinical microbiology reviews, 16(1), pp.79-95.
Mars M.H., de Jong M.C.M., Franken P., van Oirschot J.T., 2001.Efficacy of a live glycoprotein E-negative bovine herpesvirus 1 vaccine in cattle in the field. Vaccine, 19 (15-16), pp.1924-1930.
Muylkens, B., Thiry, J., Kirten, P., Schynts, F. and Thiry, E., 2007. Bovine herpesvirus 1 infection and infectious bovine rhinotracheitis. Veterinary research, 38(2), pp.181-209.
Pastoret, P.P., Aguilar-Setien, A., Burtonboy, G., Mager, J., Jetteur, P. and Schoenaers, F., 1979. The effect of repeated treatment with dexamethasone on the re-excretion pattern of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus and humoral immune response. Veterinary Microbiology, 4(2), pp.149-155.
Petrini S, Iscaro C, Righi C. Antibody Responses to Bovine Alphaherpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1) in Passively Immunized Calves., 2019. Viruses, 11(1) 23.
Spilki, F.R., Esteves, P.A., Lima, M.D., Franco, A.C., Chiminazzo, C., Flores, E.F., Weiblen, R., Driemeier, D. and Roehe, P.M., 2004. Comparative pathogenicity of bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1) subtypes 1 (BHV-1.1) and 2a (BHV-1.2 a). Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira, 24(1), pp.43-49.
Stabel, J.R., Spears, J.W. and Brown Jr, T.T., 1993. Effect of copper deficiency on tissue, blood characteristics, and immune function of calves challenged with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus and Pasteurella hemolytica. Journal of animal science, 71(5), pp.1247-1255.
Vannie, P., Capua, I., Le Potier, M. F., Mackay, D. K., Muylkens, B., Parida, S., Paton, D. J., & Thiry, E., 2007. Marker vaccines and the impact of their use on diagnosis and prophylactic measures. Revue scientifique et technique (International Office of Epizootics), 26(2), 351–372.
Wentink, G.H., Van Oirschot, J.T. and Verhoeff, J., 1993. Risk of infection with bovine herpes virus 1 (BHV1): a review. Veterinary Quarterly, 15(1), pp.30-33.
Winkler, M.T.C., Doster, A. and Jones, C., 1999. Bovine herpesvirus 1 can infect CD4+ T lymphocytes and induce programmed cell death during acute infection of cattle. Journal of virology, 73(10), pp.8657-8668.