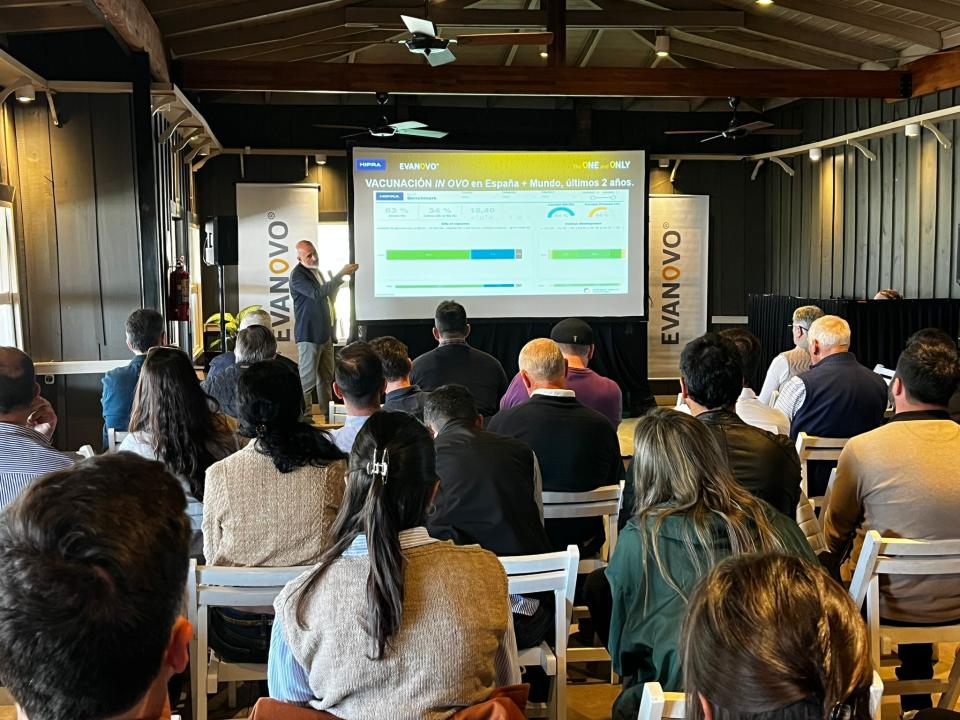
GUMBOCHECK
GUMBOCHECK is a diagnostic pack, which includes an FTA card, a form to annotate the data of sampled animals and a short guide that shows how to carry out a good sampling to obtain a positive result.
The main objective of GUMBOCHECK is to evaluate the colonization of the bursa of Fabricius by the vaccine virus, for an evaluation of the efficacy of vaccination. However, it can also be used as a diagnostic tool in the case of IBD field infection.
To achieve this, it is advisable to carry out this evaluation at different times in the life of the birds. It is recommend to be done at 21, 28 and 35 days of age. Nevertheless, when colonization of the bursa by HIPRA 1052 (GUMBOHATCH® strain) is confirmed, the subsequent sampling points may be skipped.
GUMBOCHECK STEPS
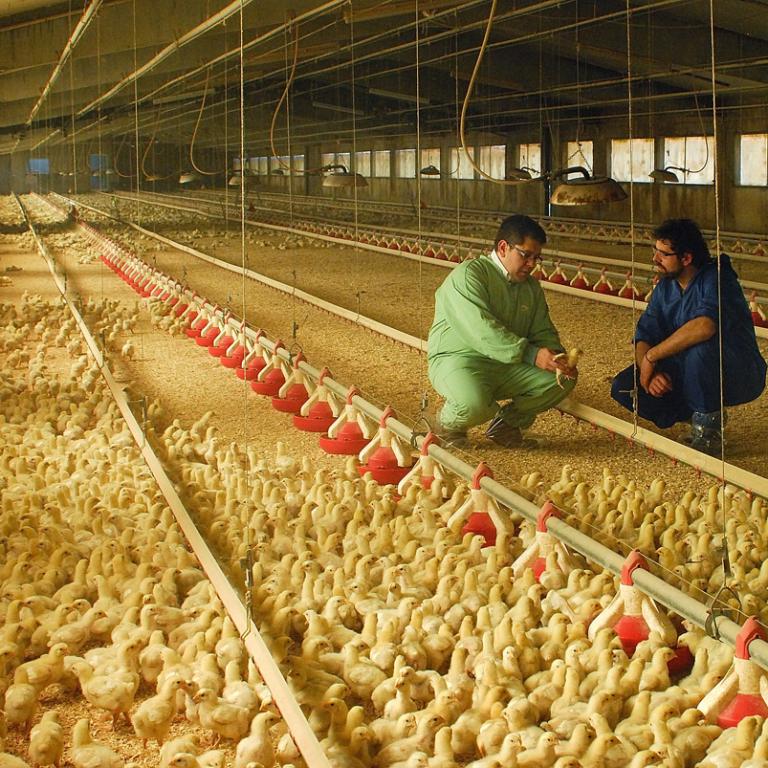
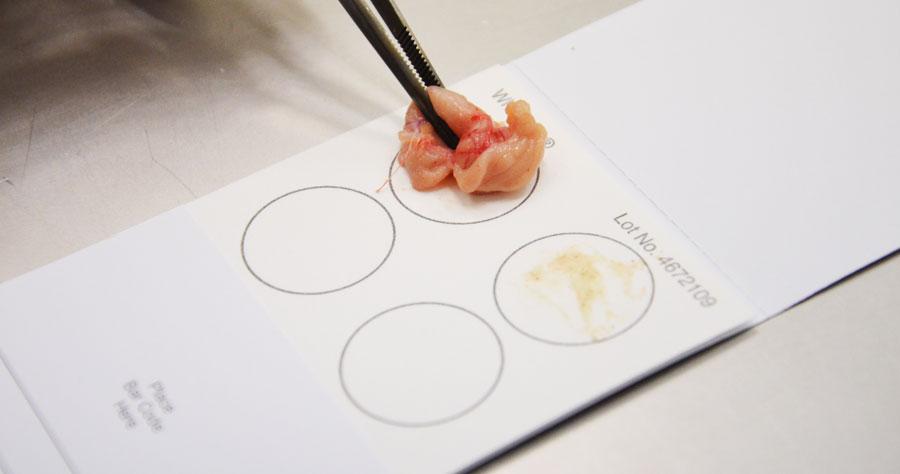
1. SAMPLING
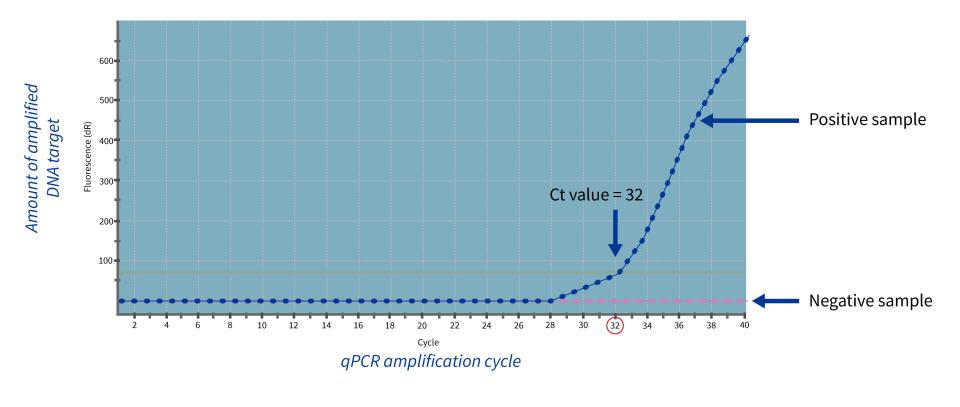
The sampling of IBD is performed with an FTA card. What is an FTA card and how does it work?
-
An FTA card is a piece of paper with a cellulose matrix designed to capture cells inside the biological samples.
-
After this capture, the membranes of the cells break (bacterial walls or the viral capsids), which facilitate the stability of the genetic material at room temperature for a long time.
-
Due to the rupture of these membranes, biological samples inoculated in FTA cards are considered as non-infectious substances, since the pathogens are inactivated.
-
FTA cards facilitate the shipment and storage of biological samples.
-
Once the FTA card arrives at the laboratory, the genetic material is easily extracted to perform the PCR.