AETIOLOGY:
Coronavirus, RNA virus, non-haemoagglutinant. It is a virus with a high capacity of recombination; it is thermolabile and sensitive to disinfectants. There are numerous serotypes.
TRANSMISSION:
- Direct: by contact with secretions or by aerosols.
CLINICAL SIGNS:
- Respiratory: coughing and sneezing in young poults.
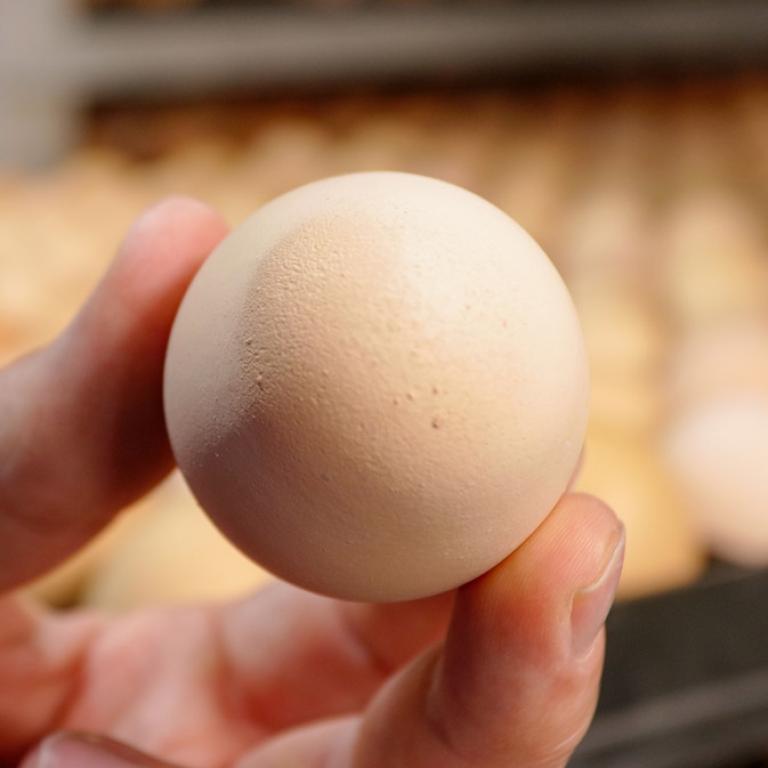
- Reproductive: alterations in the shell and internal quality of eggs in adult birds. Diagnosis by observation of clinical signs is difficult due to its lack of specificity.
LESIONS:
- Respiratory: congested trachea with accumulations of exudates.
- Reproductive: oviduct and ovarian alterations, which give rise to egg drop and problems of shell quality.
- Renal: kidneys may be damaged depending on the characteristics of the strain involved.
DIAGNOSIS:
- Causal agent identification: Isolation and identification of virus, PCR.
- Serological: ELISA, IHA, SN.
TREATMENT, PREVENTION AND CONTROL:
Antibiotic treatments are recommended against secondary agents, which may proliferate after viral infection. Live and inactivated vaccines give good results in preventing the disease. It is important not to use vaccines that include serotypes that are different from those that have been previously detected on a farm.