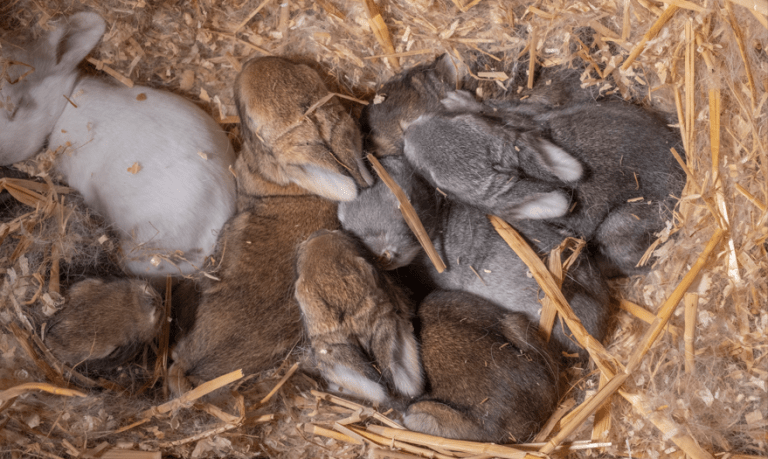
Temporal evolution of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) and impact of vaccination during the RHD epidemic in Spain (2013-2015)
World Rabbit Congress, 2016
The results of this study, in agreement with other recent publications, support the fast spread of RHDV-2, and the displacement of classical RHDV in Spain. It also provides new insights on the role of vaccination in the virus spread during the RHD epidemic. A geographical and temporal association was observed regardless of the vaccination program that was established. It is necessary to continue implementing surveillance and vaccination programs in order to control the epidemiological evolution and reduce the economic consequences of this disease.
In 2010 a new variant of rabbit haemorrhagic disease (RHDV-2) emerged in France and quickly spread through several European countries, causing atypical outbreaks in commercial rabbitries. Classical RHDV vaccines showed low cross-protection against RHDV-2, revealing the need for a specific vaccine against the disease. In this study the efficacy and safety of ERAVAC, an inactivated vaccine developed by HIPRA for preventing RHDV-2, was evaluated and compared with its simultaneous administration with a classical RHDV vaccine (Cunipravac RHD).
These results suggest that the administration of ERAVAC® alone or simultaneously with CUNIPRAVAC® RHD can be considered safe in terms of local and general reactions. Furthermore, in both cases the seroconversion induced in vaccinated rabbits confers complete protection against challenge with virulent RHDV-2 seven days after vaccination, demonstrating that the simultaneous administration of both vaccines does not interfere in the serological response against RHDV-2.