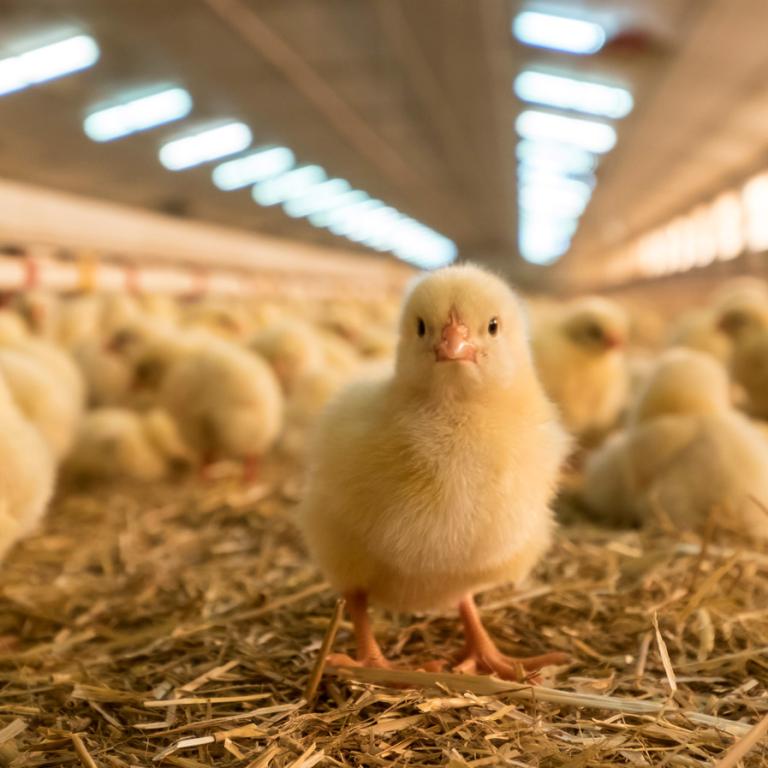
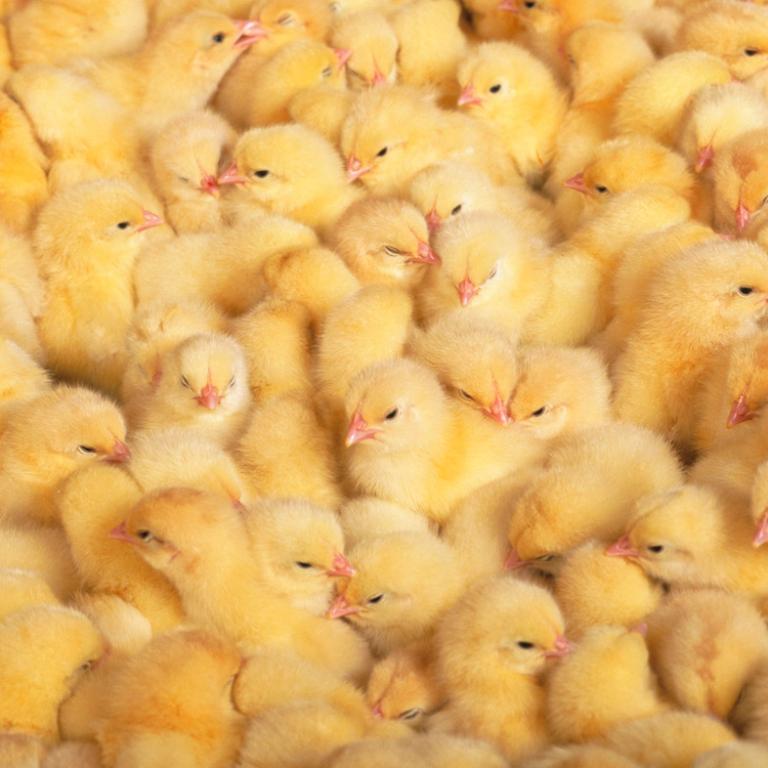
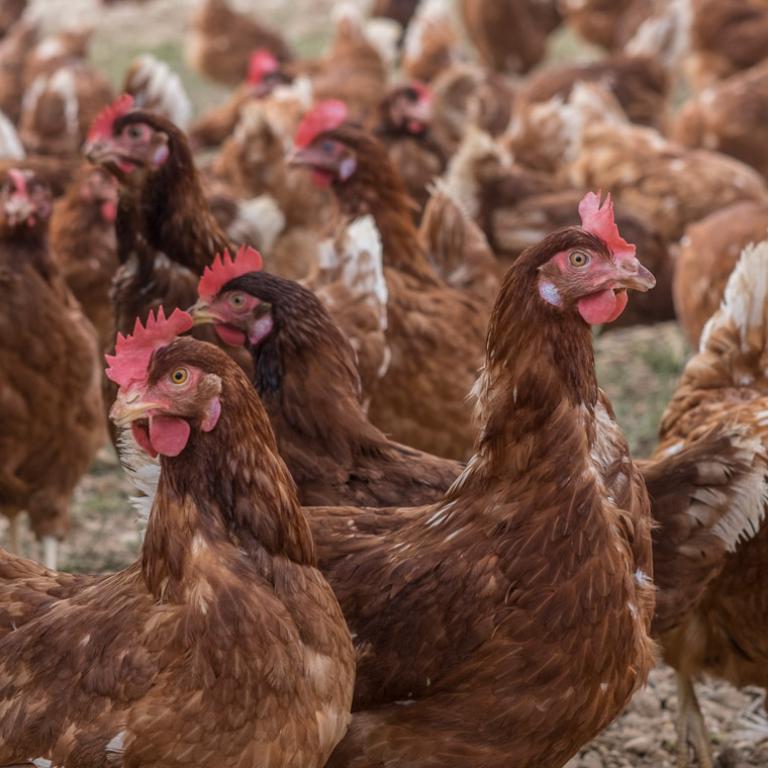
IBDV immune-complex vaccines are considered to be an intelligent tool in the prevention of Gumboro disease. These vaccines do not just offer the efficacy of a live virus (without being neutralized by maternally derived antibodies), but their onset of immunity is adapted to the protective needs of each individual chick, which avoids the feared immunity gap that can happen when other types of vaccines are used1.
Immune-complex vaccines against IBDV are formulated on the basis of adding specific IBDV antibodies (IgY) that coat the vaccine virus. From the first immune-complex vaccines developed in the 1990s until now, all available commercial immune-complex vaccines have used specific IgY extracted from the serum of hyperimmunized animals as coating antibodies (Figure 1).